Vet’s 2025 Guide to Canine Synechiae (Iris Adhesions) 🐶✨🩺
In this article
Vet’s 2025 Guide to Canine Synechiae (Iris Adhesions) 🐶✨🩺
By Dr. Duncan Houston BVSc
💡 What Are Synechiae?
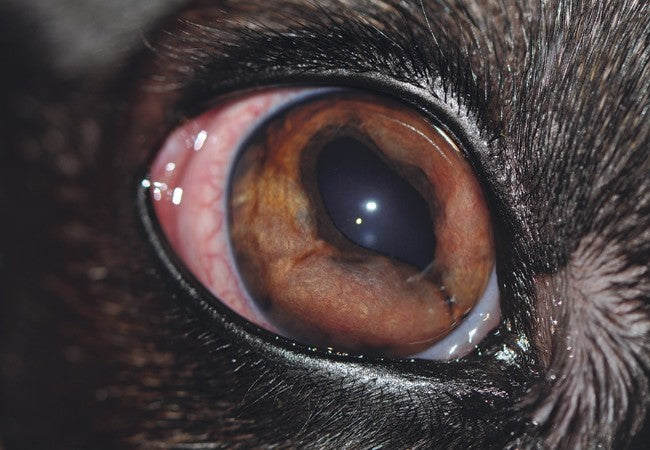
Synechiae are adhesions between the iris and lens (posterior synechia) or iris and cornea (anterior synechia). They result from intraocular inflammation (uveitis), trauma, or glaucoma, which lets fibrinous deposits “stick” internal structures together. This can impair pupil function, worsen glaucoma, and risk vision loss.
🚩 Causes & At-Risk Dogs
- 🔴 Uveitis (infectious, autoimmune): #1 cause—fibrin exudate adheres iris to adjacent tissue.
- ⚠️ Eye trauma or surgery: fibrin or blood clots foster adhesions.
- 🟠 Glaucoma: pressure changes cause iris-lens stickiness.
- 🟡 Anterior lens luxation, intraocular tumors, cataracts: also potent triggers.
- 👉 Affects any breed—especially those prone to uveitis (American Cocker Spaniel, Dachshund, Beagle).
👀 Clinical Signs
- 😣 Red eye, squinting, tearing, discharge from uveitis.
- 🕳 Pupil abnormalities: irregular shape, nonreactive “seclusion pupil”, small pupil (miosis).
- 🌡 Corneal edema, haze.
- 👁 Increased intraocular pressure, causing pain, cloudiness.
- 🔍 Vision loss or reduced light reflex depending on adhesion severity and duration.
🧪 Diagnostic Approach
- 🔬 Slit-lamp biomicroscopy to view iris-lens/cornea adhesions; fluorescein exam for corneal health.
- 📈 Tonometry to measure intraocular pressure (assess glaucoma).
- 🔍 Indirect ophthalmoscopy post-mydriasis to assess lens, retina.
- 🟨 Ultrasound (B-mode) if cornea is opaque, to evaluate lens position and detect hidden tumors.
- ⚕️ Systemic work-up—including blood testing for infectious causes (tick-borne, fungal, immune disease), chest imaging for neoplasia.
🛠 Treatment Plan
1. Medical Management
- 💊 Aggressive anti-inflammatory therapy: topical corticosteroids (e.g., prednisolone acetate), systemic options as needed.
- 💧 Cycloplegic agents (e.g., atropine) to dilate the pupil and prevent new adhesions.
- 🧪 Treat underlying infection or systemic disease (e.g., antifungals, antibiotics, immune suppression).
- 📅 Early treatment (<48 hrs) may reverse synechia—old ones need surgical removal.
2. Surgical Options
- 🔧 Synechiolysis: breaking adhesions mechanically or using viscoelastic agents under anesthesia.
- 🔫 Laser iridotomy/iridoplasty: employs laser to cut adhesion, improve pupil shape/function.
- ⚕️ Lens removal if posterior synechia prevents eye function and glaucoma control.
3. Glaucoma Management
- 💧 Treat elevated pressure (latanoprost, brinzolamide, mannitol).
- 🚫 Surgery (e.g., glaucoma shunt) if pressure is uncontrolled post-treatment.
📈 Prognosis & Long-Term Care
- 🟢 Early synechiae (<3 days) often reverse medically with good long-term vision.
- 🟡 Older adhesions may need surgery, but can still preserve eye function.
- 🔴 Severe chronic or recurrent uveitis with uncorrected synechiae can progress to glaucoma, cataracts, and phthisis bulbi (shrinking eye).
🏡 Ask A Vet App Home-Monitoring Tools 📲🐶
- 📅 Schedule topical medications and follow-up eye pressure checks.
- 📊 Log signs: squinting, discharge, pupil size, behavior changes.
- 📷 Upload photos (with flash) to monitor pupil symmetry.
- 🔔 Flag alerts for pain, haze, sudden vision loss.
- 📘 Guides: instillation technique, symptom checklist, uveitis prevention tips.
🔑 Key Takeaways 🧠✅
- Synechiae are problematic eye adhesions from inflammation or injury, risking vision if untreated.
- Signs include red eye, irregular pupil, and eye pain.
- Diagnose with slit-lamp exam, pressure checks, ultrasound, and systemic testing.
- Medical or early surgical intervention restores function in most cases.
- Home monitoring via Ask A Vet helps track healing, symptoms, and prevent recurrence.
🩺 Final Thoughts ❤️
In 2025, treating canine synechiae blends rapid anti-inflammatory therapy, pupil dilation, and individualized surgical or glaucoma management. Proactive home monitoring via Ask A Vet ensures early detection of sequelae like glaucoma or vision loss. With this collaborative approach, most dogs retain vision and comfort after prompt care 🐾✨.
Visit AskAVet.com and download the Ask A Vet app to set eye med reminders, log symptoms, upload pupil photos, and stay in close contact with your vet during treatment and prevention. 📲🐶






