Vet’s 2025 Guide to Perianal Adenoma in Dogs Benign Tumors & Care🐶🩺
In this article
Vet’s 2025 Guide to Perianal Adenoma in Dogs Benign Tumors & Care🐶🩺
By Dr. Duncan Houston BVSc
💡 Introduction
Perianal adenomas are the most common benign tumours found near a dog’s anus, arising from modified sebaceous (hepatoid) glands. These growths are hormonally driven—especially by testosterone—and typically affect intact male dogs, though spayed females can also be affected. While almost always benign and treatable, they can ulcerate, bleed, or recur if hormones remain unchecked, so understanding management is key for pet parents.
1. What Are Perianal Adenomas?
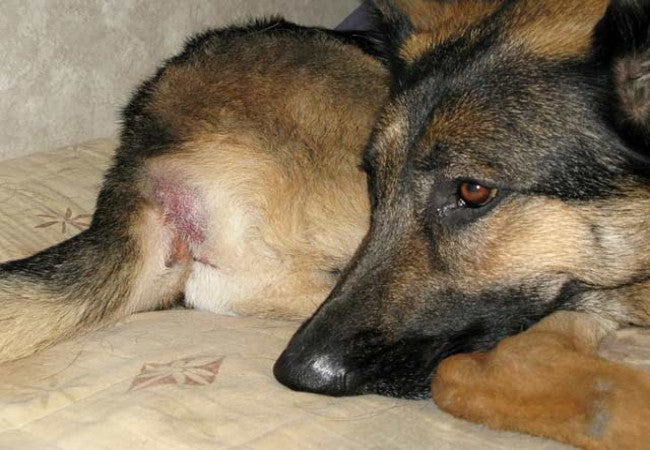
These are benign (non‑cancerous) tumors originating from perianal (circumanal/hepatoid) glands—special sebaceous glands unique to dogs. When hormonally stimulated, gland cells proliferate, forming small, round nodules around the anus, prepuce, tail base, or groin.
2. Who Is At Risk?
- Intact males: 58–96 % of perianal tumors fall into this group.
- Spayed females: Much less common but possible.
- Breeds predisposed: Siberian Husky, Cocker Spaniel, Pekingese, Samoyed, Beagle, Bulldog, German Shepherd, Afghan Hound.
- Age: Typically middle-aged to older dogs.
3. Clinical Signs & Effects
- Firm, hairless nodules around the anus—single or multiple; may ulcerate.
- Occasional bleeding or ulceration leads to licking or pruritus.
- Large tumors may cause discomfort during defecation, constipation, or straining.
- Infection, swelling, or secondary signs like soiling may accompany ulceration.
4. Diagnosis 🔍
- Physical exam: Easily palpable nodules by the vet.
- Fine needle aspirate (FNA) or cytology—reveals hepatoid cells, but need biopsy to rule out adenocarcinoma when suspicious.
- Biopsy: Gold standard if mass is atypical, large, or in females/altered dogs.
5. Treatment Strategies (2025) ❤️
5.1 Castration (Intact Males)
Neutering is the first-line treatment—it removes the hormonal stimulus, and over 90 % of tumors regress without surgery.
5.2 Surgical Removal
Used when masses: ulcerate, bleed, are large, or don't regress post-neutering. Techniques include:
- Local excision: for isolated, small tumors.
- Cryosurgery or laser ablation: options when surgery might affect continence.
- Radiation therapy: rarely needed—typically reserved for aggressive or unreachable tumors.
5.3 Female Dogs & Spayed Males
Without testosterone-driven regression, surgical removal is often necessary. Castration may still be protective.
6. Prognosis & Recurrence
- Excellent for most benign adenomas—recurrence risk low if castrated and excised.
- Adenocarcinomas (malignant) require aggressive treatment and may metastasize or recur.
- Post-removal, regular monitoring every 6–12 months helps detect changes early.
7. Preventive Advice 🔒
- Neuter dogs before 1 year old to prevent hormone-driven tumors.
- Routine rectal/perianal checks during annual exams.
- Watch for new lumps, ulcerations, bleeding, or straining behavior.
8. Ask A Vet Support 🩺
- Track lump size, bleeding, or changes via photo uploads.
- Set reminders for surgery or neuter appointments.
- Receive alerts if nodules grow post-treatment or if new masses appear.
- Access information on cryosurgery, laser options, or referral to surgeons.
🔍 Key Takeaways
- Perianal adenomas are benign, hormonally driven tumors common in intact male dogs.
- Diagnosis via FNA or biopsy; castration is core to treatment.
- Surgical removal required when tumors don’t regress, ulcerate or persist.
- Prognosis is excellent; malignant forms need aggressive therapy.
- Ask A Vet app helps track recovery, monitor recurrence, and guide follow‑up care.
🩺 Conclusion ❤️
Perianal adenomas may look concerning, but with modern veterinary care and early neutering, they are easily treated. In 2025, vets can confidently guide owners through diagnosis, removal, and prevention. Your dog can stay healthy and comfortable, with the Ask A Vet app supporting monitoring and follow-up every step of the way. 🐾✨
Dr Duncan Houston BVSc – empowering owners with smart, compassionate cancer care.
Visit AskAVet.com and download the Ask A Vet app for personalized tumor tracking, treatment reminders, and peace-of-mind through your dog’s health journey. ❤️






