Veterinary Guide to Tick-Borne Diseases in Dogs 2025: Prevention, Diagnosis & Treatment 🐶🛡️
In this article
Veterinary Guide to Tick-Borne Diseases in Dogs 2025: Prevention, Diagnosis & Treatment 🐶🛡️
By Dr. Duncan Houston BVSc
🔍 Why Tick-Borne Diseases Matter
Ticks carry multiple pathogens that affect dog health—and some spread to humans. Disease incidence is growing due to climate change, tick habitat expansion, and increased pet outdoor access.
🧭 Common Tick-Borne Diseases in Dogs
🟢 Lyme Disease (Borrelia burgdorferi)
- Transmitted by deer (blacklegged) ticks.
- Signs: shifting lameness, fever, lethargy, swollen joints, lymph nodes.
- Diagnosis: antibody-based SNAP tests; confirm with C6 or Western blot.
- Treatment: doxycycline 4–6 weeks + anti-inflammatory support.
🟠 Ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia spp.)
- Spread by brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus).
- Acute phase: fever, lethargy, weight loss, lymphadenopathy, nosebleeds.
- Chronic: pancytopenia and bleeding disorders.
- Treatment: doxycycline/minocycline 4–6 weeks; steroids for severe cases.
🟣 Anaplasmosis (Anaplasma phagocytophilum, platys)
- By deer or brown dog ticks.
- May cause fever, joint pain, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, and seizures.
- Treated similarly to ehrlichiosis—doxycycline 4 weeks.
🔴 Babesiosis (Babesia canis)
- Blood parasite transmitted by brown dog tick.
- Signs: fever, anemia, jaundice, dark urine.
- Treatment: antibabesial drugs (imidocarb), possible transfusions.
🟡 Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Rickettsia rickettsii)
- Spread by American dog, wood, brown dog ticks
- Symptoms: fever, joint pain, lymphadenopathy, neurological signs.
- Doxycycline is the drug of choice.
🔎 Key Clinical Signs Across Diseases
- Fever, lethargy, poor appetite, weight loss
- Joint pain/lameness, swollen lymph nodes
- Pale membranes (anemia), bleeding tendencies
- Neurological signs: seizures, ataxia
- Hepatomegaly, jaundice in babesiosis
🩺 Diagnosing Tick-Borne Disease
- History of tick exposure or bitten
- Physical exam findings
- Snap/blood tests for Lyme, Ehrlichia, anaplasma, RMSF
- Confirmatory panels & PCR if needed
- Bloodwork/urine evaluations for anemia or organ involvement
🛡️ Prevention Strategies in 2025
Year-round tick protection is essential—no true safe season.
- Tick preventives: isoxazoline chews (Simparica Trio), topicals, Seresto collars.
- Vaccines: Lyme vaccines beneficial in high-risk areas if combined with preventives.
- Environmental management: mow lawn, clear leaf litter, treat habitat with repellents.
- Tick checks: daily focus on ears, collar area, toes, groin.
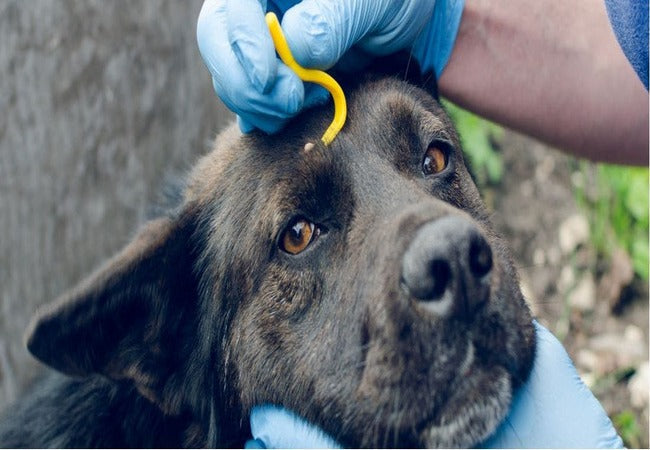
- Proper removal: fine tweezers, steady pull, save tick, disinfect area.
- Protective clothing & repellents: permethrin-treated gear; natural repellents supplemented.
💉 Treatment Approaches
- Doxycycline: 4–6 weeks is primary therapy for bacterial TBDs.
- Babesiosis: imidocarb, atovaquone, transfusion support.
- Supportive care: fluids, pain relief, NSAIDs.
- Co-infections: frequent; treat multiple pathogens concurrently.
🏠 Home Care & Monitoring
- Ensure hydration & appetite post-treatment
- Limit intense activity during recovery
- Recheck labs after therapy ends
- Continue preventives and tick checks
📈 Public Health Perspective
Dogs are sentinels—protecting them limits human risk from Lyme, RMSF, ehrlichia; coordinated efforts via AKC CHF and CDC improve surveillance.
🛠️ Role of Ask A Vet
- Ask A Vet: Offers expert guidance for prevention protocols, tick removal best practices, early signs, and antibiotic timing.
🆕 New 2025 Trends
- Expanded tick species range—watch for longhorned and Haemaphysalis ticks.
- Genetic tick-resistant dog collars entering market.
- Wearable monitors track dog vital signs to preempt disease onset.
- Improved PCR diagnostics deliver faster, precise pathogen detection.
👣 Quick Action Checklist
- Administer year-round tick prevention
- Conduct daily tick checks after outdoor time
- Remove ticks properly ASAP
- Watch for fever, lameness, appetite changes
- Seek vet evaluation and testing if signs appear
- Start antibiotics promptly; supportive care as needed
- Reassess with lab follow-up
- Maintain prevention and monitoring
👨⚕️ Final Thoughts from Dr Duncan
Tick-borne diseases are preventable and treatable when caught early. In 2025, integrated strategies—effective preventives, proper removal, vigilant health checks, and remote veterinary access—offer robust protection for dogs and families. Let’s stay proactive and safer together. 💙
Visit AskAVet.com or download the Ask A Vet app for 24/7 vet support—whether it’s a tick bite, disease concern, or prevention plan.






